What is Iris Scanning?
Iris recognition biometric systems apply mathematical pattern-recognition techniques to images of the irises of an individual’s eyes. Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual’s eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance.
Retinal scanning is a different, ocular-based biometric technology that uses the unique patterns on a person’s retina blood vessels and is often confused with iris recognition. Iris recognition uses video camera technology with subtle near-infrared illumination to acquire images of the detail-rich, intricate structures of the iris which are visible externally. Digital templates encoded from these patterns by mathematical and statistical algorithms allow the identification of an individual or someone pretending to be that individual. Databases of enrolled templates are searched by matcher engines at speeds measured in the millions of templates per second per (single-core) CPU, and with remarkably low false match rates.

Several hundred million persons in several countries around the world have been enrolled in iris recognition systems for convenience purposes such as passport-free automated border-crossings and some national ID programs. A key advantage of iris recognition, besides its speed of matching and its extreme resistance to false matches, is the stability of the iris as an internal and protected, yet externally visible organ of the eye.
How do iris scanners work?
Fun fact: having eyes of two different colors is a real condition. It is called heterochromia iridium and is found in less than 1% of the world’s population. Brown is the most common eye color, while green, amber, and silver are three of the rarest. The iris is that beautiful part of the eye that determines the eye’s color. If you look at yours from up close, you’ll notice the intricate, wavy lines on its surface, spanning in and out, from its outer to its inner perimeter. These lines form a pattern, and that is what an iris scanner “reads” to tell that you are you. This series of lines and waves is highly complex. It generates randomly and doesn’t change with time. Therefore, it is safe to say that every person’s eye is unique. Even your left and right eye have their individual iris patterns!
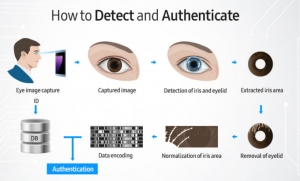
But an iris scanner doesn’t just take a picture of your eye to compare against whatever it has on record. In actuality, the procedure starts with a beam of near-infrared light directed at the person’s eye. This kind of light works better than visible light since it exposes the pattern of the iris much more clearly, thus making it easier for a camera to capture it. Besides, it allows the iris scanner to work in the dark. Prescription glasses and contact lenses (not colored!) do not block the beam either. Once the image has been recorded, an intelligent piece of software translates the iris’ pattern into code. This code is then compared against a record in search of a match.
What makes an iris scan unique?
The iris is the colored ring of muscle that opens and shuts the pupil of the eye like a camera shutter. The colored pattern of our irises is determined genetically when we’re in the womb but not fully formed until we’re aged about two. It comes from a pigment called melanin—more melanin gives you browner eyes and less produces bluer eyes. Although we talk about people having “blue eyes,” “green eyes,” “brown eyes,” or whatever, in reality, the color and pattern of people’s eyes is extremely complex and completely unique: the patterns of one person’s two eyes are quite different from each other and even genetically identical twins have different iris patterns.
Application areas of biometric iris recognition
Finance and banking
The use of iris recognition is expected to improve standards of financial services as the bankers will become free from time-consuming document processing for identity proofs. This, in turn, will give them ample time and opportunity to concentrate on other important areas such as customer service.
Iris scanning at pos terminals
After suffering substantial losses due to card loss, merchants have begun the process of integrating iris recognition technology in POS terminals to add another level of security to their systems and reduce fraud costs. These technologies store the iris patterns of all employees and in the event of theft or unauthorized transaction can immediately isolate the employee at fault. As a result, the adoption of such biometric technology will protect merchants from fraudulent.
Healthcare and welfare
- Tracking patient registration.
- Treatment or passageways to different departments.
- Repetitive treatment.
- Checkup arrangement and scheduling.
- Supporting national or private Health Insurance Cards.
- Ambulant treatment document
Hospitality and tourism
Tourism and hospitality industry have also started taking the first steps toward biometric iris recognition-based authentication facilities. As part of such a system, guests have images of their irises recorded at the hotel concierge’s desk, and the images are stored in a database. When trying to gain access to the suite, a video-camera like a device takes a picture of the iris and matches it to the database record. Guests’ iris images stored in the database are set to expire upon checkout.
Public safety
Mobile iris recognition in law enforcement applications allows rapid identification of individuals during field operations. Utilizing the security and accuracy of iris recognition technology, law enforcement agencies can save the backdrop of contemporary security challenges bordering on terrorism, high incidence of car theft, carjacking, kidnappings and other acts of crimes and criminality in our society.
Bank ATMs
Iris-based biometric ATM’s are more secure than conventional pin based ATM’s because it requires biometric verification which cannot be stolen, copied or faked. Pin-based security systems can be compromised leading to losses for the consumer as well as the bank.
Pros:
-
Randomness: The randomness degree of iris pattern is very high which makes every iris unique. As an example, the variability iris has 244 degrees-of-freedom and the entropy has 3.2 bits per square millimeter.
-
Pupil Size: The changing pupil size confirms the natural physiology of an iris. But, the pattern of an iris doesn’t change.
- Protection: The iris is an internal organ of the eye. For this reason, iris pattern never changes in a lifetime. As an internal organ, it is highly protective compared to retina recognition.
-
Traceable: The encoding and decision making of iris pattern is highly traceable. It takes only 30 milliseconds for the image analysis and the subsequent encoding.
-
Glass/Contact lenses: A lot of people use glass or contact lenses to see things perfectly. Though these gadgets are very close to the eye, it doesn’t make any difference in the iris recognition process.
-
Fast: With the iris recognition system, a person can complete the process within just a few seconds. If the initial enrollment has taken place, it works faster than other modalities. From next enrolment, a camera will capture the iris, and then the matching system will work with the database and send the report instantly.
Cons:
-
Infrared light: The constant use of this system may cause harm to the iris because it is constantly being scanned with infrared light.
-
Location: The placement of iris is somewhat bizarre. It is situated behind a curved, wet, reflecting surface.
-
Storage: A lot of memory is required for the data to be stored and later accessed.
-
Obscure: It is obscured by eyelashes, lenses, and reflections, which create a problem, more often than not.
-
Eyelids: Iris is partially blocked by eyelids which is difficult to control by individuals due to frequent blinking.
-
Transformation: Iris may deform non-elastically as the pupil may change its size due to medical or other conditions.
| Biometric | Universality | Uniqueness | Collectability | Performance | Acceptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Face |
High | Low | High | Low | High |
|
Fingerprint |
Medium | High | Medium | High | Medium |
|
Vascular |
Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
|
Iris |
High | High | Medium | High | Low |
|
Voice |
Medium | Low | Medium | Low | High |
|
DNA |
High | High | Low | High | Low |
Conclusion
Iris recognition technology is durable, quantifiable, recordable and reliable. It thus fulfills the basic tenets of an ideal biometric system. The stored biometric template can be used for a person’s whole life as iris patterns are not susceptible to change, remaining stable for long periods of time. Enrollment is required only once in a lifetime, saving both time and money.
Biometric iris recognition systems are easy to use and create a hassle-free security environment. Iris scanners can be used to protect high-value locations by denying access to unwarranted visitors. Business and governmental organizations across the board have recognized the benefits of this system and have gone about implementing iris recognition-based authentication systems in a big way.
Author: Ravi Kumar Allaka – QA Analyst
Source: https://www.bayometric.com/biometric-iris-recognition-application/